Professional and high-quality metal alloys, ceramic products and concrete additives | RBOSCHCO
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
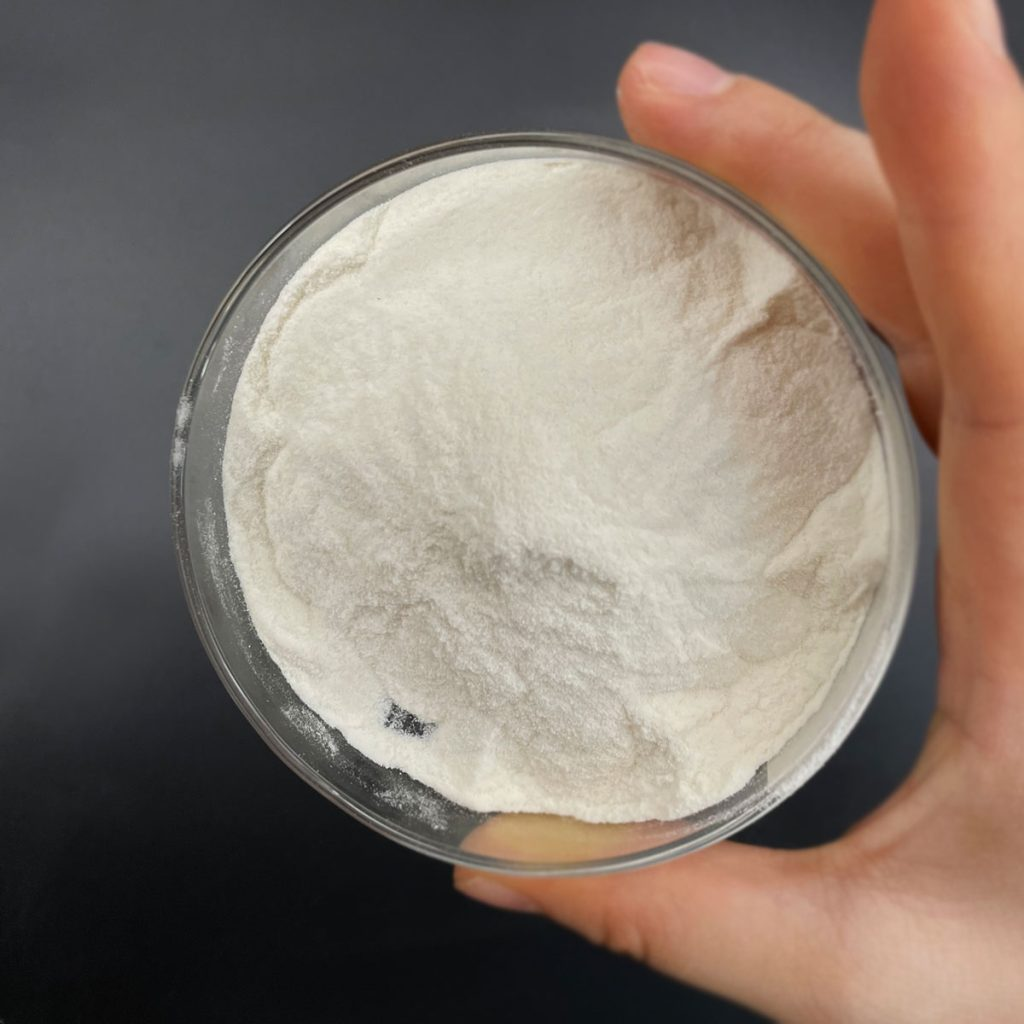
Overview of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) powder, known for its high-temperature stability and resistance to oxidation, a metal-ceramic composite material, attracts attention for its unique combination of mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. This powder finds widespread use in various industrial applications. Its unique properties make it a material of choice for high-performance and demanding engineering solutions.

(Molybdenum Silicide MoSi2 Powder CAS 12136-78-6)
Characteristics of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
High-Temperature Security: MoSi2 powder shows outstanding stability at high temperatures, preserving its mechanical properties even in severe conditions. Resistance to Oxidation: The product forms a protective oxide layer at high temperatures, preventing additional oxidation and making certain resilience. Outstanding Thermal Conductivity: MoSi2 powder uses high thermal conductivity, making it appropriate for heat transfer applications. Great Electric Conductivity: In spite of being a ceramic material, MoSi2 displays excellent electric conductivity, appropriate for use in digital tools. High Stamina and Solidity: The powder, when sintered, creates a material with high strength and firmness, appropriate for wear-resistant applications.
Parameter table of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
| Molybdenum Silicide Properties | |
| Other Names | molybdenum disilicide, MoSi2 powder |
| CAS No. | 12136-78-6 |
| Compound Formula | MoSi2 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.11 |
| Appearance | Gray to Black Powder |
| Melting Point | 1900-2050 °C |
| Boiling Point | N/A |
| Density | 6.23-6.31 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in H2O | N/A |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.0000270 – 0.0000370 ohm-cm |
| Specific Heat | 0.437 J/g-°C (23 °C) |
| Tensile Strength | 185 MPa (Ultimate) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 66.2 W/m-K (23 °C) |
| Thermal Expansion | N/A |
| Vickers Hardness | 900-1200 |
| Young’s Modulus | N/A |
| Exact Mass | 153.859261 |
| Molybdenum Silicide Health & Safety Information | |
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Codes | 20/21/22 |
| Safety Statements | 36 |
| RTECS Number | N/A |
| Transport Information | N/A |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
Application of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
Aerospace Industry: MoSi2 powder is made use of in the aerospace industry for its high-temperature security and resistance to oxidation, making it suitable for elements exposed to extreme temperature levels.
Electronics and Semiconductors: Its great electric conductivity and thermal security make it valuable in digital product packaging and semiconductors.
Thermal Protection Solutions: The product’s ability to withstand heats without oxidizing makes it ideal for thermal protection systems in spacecraft and rockets.
Mechanical Elements: MoSi2 powder is utilized in the manufacturing of wear-resistant mechanical parts, such as bearings and seals, due to its high stamina and solidity.
Energy Conversion Devices: Its high thermal conductivity and electrical properties make it suitable for use in solar cells, fuel cells, and other energy conversion devices.

Aerospace Industry
Electronics and Semiconductors

Thermal Protection Systems

Mechanical Components

Energy Conversion Devices
Production Method of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
1. Direct Synthesis
Mix molybdenum (Mo) and silicon (Si) powders in a 1:2 ratio. Heat them in a vacuum or inert gas furnace at 1600–2000°C. The reaction forms MoSi₂:
Mo + 2Si → MoSi₂. Cool and grind the product into powder.
2. Mechanical Alloying
Put Mo and Si powders in a ball mill. High-energy milling causes solid-state reactions. The powders blend and react over hours. Final heat treatment at 1200–1400°C completes the alloying.
3. Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis (SHS)
Press Mo and Si powders into pellets. Ignite them to trigger an exothermic reaction. The heat spreads, converting the mixture to MoSi₂. This method is fast but needs careful control.
4. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
React molybdenum hexacarbonyl (Mo(CO)₆) and silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄) in a high-temperature chamber (900–1200°C). Gases deposit MoSi₂ onto surfaces. Scrape off the layer to get powder.
5. Sol-Gel Method
Dissolve Mo and Si alkoxides in alcohol. Hydrolysis forms a gel. Dry and heat the gel at 800–1000°C. This produces nanoscale MoSi₂ powder with high purity.

Company Profile
RBOSCHCO is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12-year-experience in providing super high-quality chemicals and nanomaterials, including boride powder, nitride powder, graphite powder, sulfide powder, 3D printing powder, etc.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder, please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.
Storage Condition of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
Sealed Containers:Store MoSi₂ powder in airtight bags or jars. This stops moisture and oxygen from getting in, which could cause oxidation.
Dry Environment:Keep it in a dry place with low humidity (below 40%). Add desiccants like silica gel to the container if needed. Moisture can slowly break down the powder.
Avoid Acidic Materials:Do not store near acids (like HCl or H₂SO₄). These react with MoSi₂ and lower its purity.
Stable Temperature:Store at room temperature (15–25°C). High heat (over 1000°C) may change its structure, but normal storage doesn’t need special cooling.
Dust-Free Handling:Use gloves and clean tools. Avoid inhaling dust or letting it touch skin. Clean spills right away.
Label Clearly:Mark containers with the name, purity, and date. This helps track usage and prevents mistakes.
Payment Term
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.

Shipment Term
By sea, by air, by express, as customers request.
5 FAQs of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder
Q1:
What are the key benefits of using Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder?
Re: The key benefits of using Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder include its high-temperature stability, resistance to oxidation, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. These properties make it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, especially in demanding environments where traditional materials may fail.
Q2:
How is Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder processed?
Re: Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder is usually generated with a high-temperature response in between molybdenum and silicon. This reaction is meticulously controlled to guarantee the formation of an uniform and pure powder.
Q3:
What are the safety considerations when handling Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder?
Re: When taking care of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder, it is essential to put on safety tools, such as gloves and a dirt mask, to avoid inhalation or contact with the skin. In addition, the powder ought to be saved in a well-ventilated location to prevent dust accumulation.
Q4:
Can Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder be recycled?
Re: Yes, Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder can be recycled. Nonetheless, the recycling procedure might involve complicated steps such as re-melting and purification to make certain the top quality of the recycled material.
Q5:
What are the potential applications of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder in the future?
Re: The potential applications of Molybdenum Silicide (MoSi2) Powder in the future are diverse and interesting. With its one-of-a-kind mix of properties, it can find usage in advanced power conversion tools, high-temperature electronics, and also in next-generation aerospace products.
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS

Titanium Silicide Ti5Si3 Powder CAS 12067-57-1

Hollow Glass Sphere Hollow Glass Beads

Chromium Silicide CrSi2 Powder CAS 12018-09-6

Sodium Meta Silicate Silicate De Sodium Liquide Pour Savon Powder or Liquid Price CAS 1344-09-8

Liquid Lithium Silicate for Concrete Hardener and Dustproof Sealer







